frequently
asked
QUESTIONS
What is HVAC?
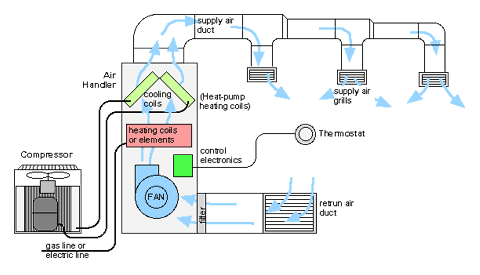
HVAC stands for Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning. HVAC is used in commercial, industrial and residential facilities. It provides fluid air through the facility providing either hot or cool air dependent on the desired temperature. This can be controlled by a thermostat which reads the temperature of the complex and acts accordingly maintaining a desired temperature for the building. Sending signals to the HVAC machines to either pump cool or hot air through the ventilation system in turn creating a clean comfortable environment.
Air conditioning is when the air is cooled to a desired temperature via a system of refrigeration or a free cooling system which uses pumps to circulate a cool refrigerant (typically water or a glycol mix). Free cooling systems can have very high efficiencies, and are sometimes combined with seasonal thermal energy storage so the cold of winter can be used for summer air conditioning.
Heating is the act of warming a building by use of increased energy generally by use of fire, chemical reaction or water. Central heating is often used in cool climates to heat houses and public buildings. Such a system contains a boiler, furnace, or heat pump to warm water, steam, or air in a central location such as a furnace room in a home or a mechanical room in a large building. The use of water as the heat transfer medium is known as hydronics. These systems also contain either duct work for forced air systems or piping to distribute a heated fluid to radiators to transfer this heat to the air.
Ventilation is the process of changing or replacing air in any space to control temperature or remove any combination of moisture, odors, smoke, heat, dust, airborne bacteria, or carbon dioxide, and to replenish oxygen. Ventilation includes both the exchange of air with the outside as well as circulation of air within the building. It is one of the most important factors for maintaining acceptable indoor air quality in buildings. Methods for ventilating a building may be divided into mechanical/forced and natural types. Without proper ventilation, carbon monoxide can be lethal at concentrations of 1000 ppm (0.1%). However, at several hundred ppm, carbon monoxide exposure induces headaches, fatigue, nausea, and vomiting.
What does System Efficiency matter?
In the past, water heating was more efficient for heating buildings and was the standard in the United States. Today, forced air systems can double for air conditioning and are more popular. This means; Better air conditioning effects, energy savings of up to 15-20%, and even conditioning flow.
Energy recovery systems sometimes utilize heat recovery ventilation or energy recovery ventilation systems that employ heat exchangers or enthalpy wheels to recover sensible or latent heat from exhausted air. This is done by transfer of energy to the incoming outside fresh air. Making your HVAC system run at peak efficiency.
Providing clean efficient air throughout the system will reduce energy costs saving money in the long run. By keeping our system clean through regular maintenance we can decrease running costs by increasing the efficiency of the system and life of the HVAC system as well.
To learn more about maximizing your system efficiency Click Here.
Comfort Air Discounters is an Equal Opportunity Employer M/F.
All qualified applicants will receive consideration for employment without regard to their
protected veteran status and will not be discriminated against on the basis of disability.
© 2014 Comfort Air Discounters Inc. All Right Reserved